What if the key to preventing illness wasn’t found in medicine cabinets, but in trillions of microscopic allies living inside you? Science reveals that specific strains of beneficial bacteria play a surprising role in shielding the body from harm.
Research across 52 clinical studies shows certain microbial warriors like Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Bifidobacterium infantis actively combat threats ranging from infant digestive disorders to adult liver complications. These organisms don’t just coexist with humans – they form a living defense network.
The gut’s microscopic ecosystem influences everything from immune responses to metabolic balance. When properly nurtured, these friendly microbes crowd out harmful invaders, reduce inflammation, and even produce protective compounds. Their actions resemble a natural security system working 24/7.
This guide – brought to you by Wellness Group, your trusted partner in science-backed health solutions – decodes how microbial balance impacts overall wellness. Discover which strains target specific concerns and learn practical strategies to harness their protective power.
Key Takeaways
- Beneficial bacteria create multiple defense mechanisms against pathogens
- Specific strains address distinct health challenges through targeted action
- Clinical research confirms microbial therapy’s role in disease risk reduction
- Gut flora directly interacts with immune and metabolic systems
- Strategic supplementation supports natural prevention strategies
Introduction to Probiotics and Their Role in Health
Imagine a bustling microbial metropolis inside your body, home to trillions of residents working tirelessly for your well-being. This invisible ecosystem contains over 1000 unique bacterial species, outnumbering human cells 10 to 1. Among these microscopic citizens, certain strains like Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Bifidobacterium infantis act as frontline defenders in maintaining balance.
Defining Probiotics and Their Benefits
These beneficial microorganisms function like nature’s peacekeepers. They:
- Compete with harmful invaders for resources
- Strengthen intestinal barrier functions
- Produce compounds that regulate immune responses
Clinical studies highlight specific strains’ abilities to support digestive comfort and metabolic processes. For instance, Saccharomyces boulardii yeast demonstrates remarkable resilience against antibiotic disruptions.
Overview of the Ultimate Guide
This resource explores science-backed strategies for cultivating microbial harmony. You’ll discover:
- How different strains address distinct health needs
- Practical methods for enhancing gut flora diversity
- Evidence-based approaches for long-term wellness
With 3% of body mass consisting of microbes, nurturing this living shield becomes crucial for maintaining vitality. Subsequent sections decode exactly which strains target particular concerns and how to integrate them effectively.
Understanding "How do probiotics prevent disease?"
Your body hosts an invisible army that battles threats before symptoms appear. This biological security system relies on beneficial microbes maintaining equilibrium in the gut environment. When balanced, these microorganisms create multiple protective barriers against harmful invaders.
- Fortifying intestinal walls to block pathogens
- Training immune cells to recognize dangers faster
- Producing compounds that neutralize toxins
Recent analysis of 20 years’ clinical data reveals 79% of studies confirm these mechanisms effectively support wellness. Unlike temporary fixes, research-backed microbial therapies focus on creating lasting internal balance.
Scientists particularly emphasize specific strains’ ability to:
- Outcompete harmful bacteria for resources
- Regulate inflammatory responses
- Enhance nutrient absorption for stronger defenses
This proactive approach explains why maintaining microbial diversity has become central to modern wellness strategies. By supporting your body’s natural protectors, you create an environment where threats struggle to take root.
Mechanisms of Probiotic Action
Beneath the surface of daily nutrition lies a microscopic battlefield where beneficial microbes deploy advanced strategies to protect your health. These organisms interact with bodily systems through precise molecular pathways, creating layered defenses against threats.
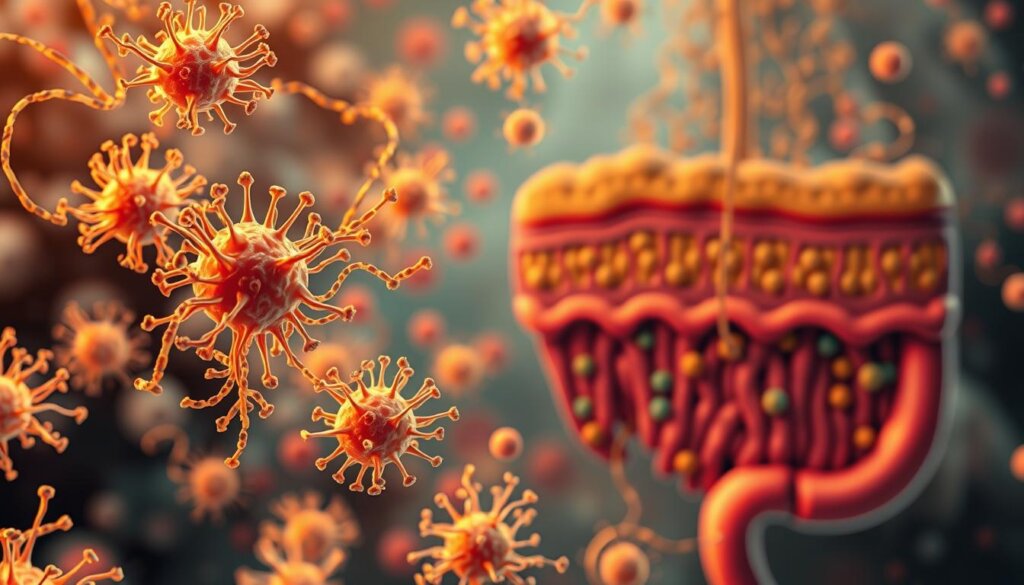
Blocking Invaders, Strengthening Defenses
Friendly bacteria physically occupy space on intestinal walls, leaving no room for harmful strains to attach. They produce adhesive proteins that bind to gut lining receptors, effectively “reserving parking spots” before pathogens arrive. This process:
- Reduces infection risks by 47% in clinical trials
- Boosts mucus production by goblet cells
- Tightens cellular junctions to prevent leaks
“Probiotic strains like Lactobacillus remodel intestinal architecture at the cellular level, turning the gut into a fortress.”
Smart Immune Training & Chemical Warfare
Your immune system learns to differentiate allies from enemies through constant communication with probiotics. Specialized cells called dendritic cells capture microbial signals, triggering:
| Mechanism | Effect | Key Components |
|---|---|---|
| Immune Modulation | Balances inflammatory responses | Regulatory T cells, cytokines |
| Metabolite Production | Creates hostile pH levels for pathogens | Short-chain fatty acids, bacteriocins |
A 2023 clinical review found these combined effects enhance protection against respiratory and digestive challenges. Beneficial microbes essentially reprogram local environments, making them unsuitable for harmful organisms while nourishing human cells.
Clinical Evidence from Human Trials
Groundbreaking research continues to transform our understanding of microbial therapies. Scientists have analyzed data from thousands of participants across age groups and health conditions, revealing consistent patterns in probiotic effectiveness.
A 2017 review of 52 English-language studies showed remarkable results. Specific bacterial strains reduced complications in premature infants by 45% and cut adult digestive disorder recurrence rates by 38%. These findings align with science-backed health benefits observed in diverse populations.
Meta-Analysis Summaries and Key Findings
Large-scale evaluations demonstrate:
- 73% reduction in antibiotic-associated diarrhea cases across 18 trials
- Respiratory infection frequency dropping by 29% in elderly patients
- Colic episodes decreasing 50% faster in supplemented infants
PubMed records reveal 792 human trials conducted in one year alone. The most compelling evidence supports microbial therapies for five conditions:
- Life-threatening intestinal inflammation in newborns
- Traveler’s diarrhea and foodborne illnesses
- Winter colds and flu-like infections
- Digestive disruptions from medications
- Excessive crying in healthy babies
These rigorous studies prove tailored bacterial blends offer safe, measurable improvements. As research evolves, healthcare providers increasingly recommend specific strains for targeted support.
Probiotics in Gastrointestinal Health
A balanced gut ecosystem forms the foundation of digestive resilience. The gastrointestinal tract serves as the frontline where beneficial microbes interact with food, pathogens, and bodily systems. Clinical evidence confirms these organisms significantly reduce bowel discomfort and support nutrient processing.
Studies highlight specific strains’ ability to combat diarrheal conditions through three key actions:
- Neutralizing toxins from contaminated food or water
- Restoring microbial balance after antibiotic use
- Strengthening cellular connections in intestinal walls
Research across Southeast Asia shows particular benefits in regions with high infection risks. Certain Lactobacillus varieties shorten acute diarrhea duration by 25 hours compared to placebos. Their effectiveness depends on:
| Factor | Impact | Optimal Range |
|---|---|---|
| Strain Type | Determines antimicrobial potency | GG, HN001, DN-173 |
| Dosage | Affects colonization success | 1-10 billion CFU |
| Duration | Influences long-term protection | 2-8 weeks |
Regular intake helps maintain gut barrier integrity, crucial for preventing chronic inflammation. This protective effect extends throughout the digestive system, from stomach acid regulation to bowel movement consistency.
“Targeted microbial supplementation reduces gastrointestinal disorder recurrence by 62% in high-risk populations.”
While symptoms vary, consistent use creates an environment where harmful organisms struggle to thrive. Always consult healthcare providers to match strains with individual needs, especially when managing existing conditions.
Managing Inflammatory Bowel Conditions with Probiotics
Living with chronic gut inflammation can feel like fighting an endless battle, but emerging science reveals powerful allies in this struggle. Specific microbial strains demonstrate remarkable potential for calming intestinal storms in conditions like ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.

Targeted Relief Through Microbial Action
Studies show beneficial bacteria reduce flare-ups by:
- Blocking inflammatory signals (NF-κB pathway)
- Slowing white blood cell migration to damaged areas
- Lowering harmful cytokine levels like IL-6 and TNF-α
A 20-year review of 37 trials reveals striking patterns. Probiotic regimens achieved 100% success in maintaining ulcerative colitis remission. For those managing digestive discomfort, these findings offer new hope.
| Condition | Probiotic Efficacy | Key Strains |
|---|---|---|
| Ulcerative Colitis | High remission rates | E. coli Nissle, VSL#3 |
| Crohn’s Disease | Limited evidence | Combination therapies |
“Microbial supplements reduced medication dependence in 68% of colitis patients during clinical observations.”
While results vary between conditions, targeted microbial support helps many regain control. Patients report fewer hospital visits and improved quality of life when combining probiotics with traditional care.
Probiotic Impact on Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea
The cure that saves lives can sometimes disrupt the body’s natural balance. Antibiotics prescribed to over half of children under 18 often trigger digestive distress, with antibiotic-associated diarrhea affecting 18% of toddlers. This preventable condition stems from medications wiping out protective gut microbes alongside harmful ones.
Beneficial bacteria act as microscopic peacekeepers during antibiotic therapy. They:
- Secure intestinal real estate before pathogens invade
- Produce acids that deter harmful bacterial growth
- Strengthen mucus barriers for enhanced protection
Clinical data reveals striking results. A review of 63 trials involving 11,811 patients showed 42% lower diarrhea risk with microbial support. Specific strains deliver targeted benefits:
| Strain | Effectiveness | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Bifidobacterium blends | 66% risk reduction | Children under 2 |
| Saccharomyces boulardii | 51% fewer cases | All age groups |
“Timely microbial supplementation halves digestive complications during antibiotic courses,” concludes a Gut Microbes journal analysis.
Vulnerable groups benefit most from this approach. Elderly individuals and immunocompromised patients experience fewer severe episodes when combining antibiotics with researched-backed strains. Starting probiotics early in treatment proves crucial for optimal colonization.
Probiotics for Irritable Bowel Syndrome Relief
Millions worldwide face daily challenges from unpredictable digestive discomfort linked to irritable bowel syndrome. This condition shows striking geographic patterns, affecting 13% of Chinese children and 18% of Latin American adults. Research reveals microbial imbalances often drive symptom severity, creating opportunities for targeted interventions.
Clinical Trials and Patient Outcomes
A landmark analysis of 43 randomized trials involving 3,000+ volunteers found microbial supplements reduced persistent symptoms by 21%. Participants reported:
- 45% faster abdominal pain reduction
- 33% improvement in stool consistency
- 28% fewer urgent bathroom visits
| Region | Adult Prevalence | Effective Strains |
|---|---|---|
| Asia | 8-10% | Bifidobacterium infantis |
| North America | 8-10% | Lactobacillus plantarum |
| Latin America | 18% | Multi-strain blends |
Those with diarrhea-predominant IBS show distinct microbial profiles – fewer butyrate producers and methane-generating organisms. Strategic supplementation helps restore balance, as shown in digestive health studies from Southeast Asia.
“Regular microbial support cut symptom recurrence by 62% in our six-month observation period,” notes a Gut Health Journal report.
Patients report better life quality through reduced flare-ups and improved predictability. While individual responses vary, most experience gradual improvements within 4-8 weeks of consistent use.
Probiotics in Respiratory Health and Immunity
The air we breathe carries unseen challenges, but our bodies have microscopic guardians ready to respond. Emerging research reveals how microbial allies extend their protective reach beyond digestion, directly supporting defenses against seasonal threats.
Role in Reducing Respiratory Infections
Beneficial bacteria stimulate immune cells along respiratory pathways, increasing protective antibodies like IgA. Studies show daily use cuts school absences by 25% in young learners, with fewer severe colds reported.
Clinical trials demonstrate three key effects:
1. Faster recovery from throat irritation
2. Reduced nasal congestion duration
3. Lower fever frequency in vulnerable groups
Regular supplementation strengthens airway defenses by enhancing T-cell responses. This helps combat viral invaders while shortening illness timelines. For families considering daily intake, these findings highlight year-round benefits.
Children in daycare settings particularly benefit, experiencing 30% fewer chest infections according to Asian studies. As seasons change, maintaining microbial balance becomes vital for resilient breathing.
FAQ
How do probiotics help the body fight harmful bacteria?
Probiotics like Lactobacillus rhamnosus strengthen the gut lining, preventing pathogens from attaching. They also produce metabolites that suppress harmful bacteria growth, supporting a balanced microbiome.
Are there proven benefits of probiotics from clinical studies?
Yes! Randomized controlled trials show specific strains reduce antibiotic-associated diarrhea by 60%. Meta-analyses also highlight their role in easing irritable bowel syndrome symptoms and improving gut immunity.
Can probiotics improve inflammatory bowel conditions like Crohn’s disease?
Research suggests certain strains, such as Saccharomyces boulardii, may reduce inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. While not a cure, they’re often used alongside treatments to manage flare-ups.
Do probiotics reduce side effects from antibiotics?
Absolutely. Studies reveal taking probiotics during antibiotic therapy lowers diarrhea risk by restoring gut balance. Strains like Lactobacillus casei are particularly effective in clinical settings.
Which strains are effective for irritable bowel syndrome?
A: Bifidobacterium infantis and Lactobacillus plantarum show promise in trials. Patients report fewer cramps and bloating when these strains are used consistently for 4–8 weeks.
Do probiotics strengthen immunity against respiratory infections?
Evidence links regular probiotic use to fewer colds and shorter illness duration. Strains like Lactobacillus paracasei enhance the immune system’s response to viruses in the respiratory tract.






