Wellness Group: Enhancing Fiber and Cardiovascular Health
What if a single dietary change could slash heart-related mortality risks by nearly 30%? Recent studies reveal that strategic nutrition choices may reduce life-threatening complications more effectively than many realize. Research spanning 135,000 participants shows those prioritizing specific nutrients experience up to 28% lower rates of critical health events.
Wellness Group bridges cutting-edge science with everyday habits through personalized guidance. Their approach transforms complex research into practical steps for lasting wellness improvements. Clients gain access to meal plans and evidence-based strategies that align with global health recommendations.
This guide unlocks the science behind nutrient optimization for heart protection. Readers will discover:
- How specific food components combat inflammation
- Optimal daily intake ranges for maximum benefit
- Cultural adaptations for Malaysian dietary preferences
Available for consultations via WhatsApp (+60123822655), Wellness Group simplifies preventive care through actionable nutrition plans. Their methods empower individuals to take control using sustainable, research-backed solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Dietary adjustments may reduce critical health risks by over 25%
- Personalized nutrition plans adapt to regional food traditions
- Scientific strategies require fewer than 3 weekly habit changes
- Professional guidance improves long-term commitment
- Preventive approaches cost 76% less than reactive treatments
Understanding Cardiovascular Health and Dietary Fiber

Click to 了解更多
Heart-related conditions affect millions globally, with elevated cholesterol and blood pressure being key concerns. Nearly 1 in 4 American adults face cholesterol levels above 240 mg/dL, while 28% battle hypertension. These silent threats significantly increase risks for severe circulatory system disorders.
Plant-derived nutrients that resist digestion play crucial roles in maintaining vascular function. These undigested components help manage cholesterol absorption and support healthy blood flow. Research reveals individuals consuming the most of these nutrients experience:
| Intake Level | Mortality Reduction | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High | 16-23% | Lower all-cause death risk |
| Low | Baseline | Increased disease potential |
Modern diets often lack sufficient amounts of these protective plant elements. This deficiency correlates strongly with rising cases of circulatory system issues worldwide. Regular consumption helps regulate two critical factors:
- Cholesterol management through binding mechanisms
- Blood pressure moderation via improved vessel elasticity
Emerging evidence suggests simple dietary adjustments could prevent numerous heart-related incidents. Including more whole grains, legumes, and vegetables offers practical protection against developing serious circulatory conditions.
Importance of Fiber in Maintaining Heart Health
Protecting your heart could be as simple as choosing the right foods. Studies show those eating more plant-based nutrients reduce their mortality risk by 16-23% compared to low consumers. This natural defense works through multiple biological pathways simultaneously.
These undigested plant components act like sponges in your gut. They bind excess bile acids, forcing the body to use cholesterol reserves for bile production. This process naturally lowers harmful cholesterol levels without medication.
| Daily Intake Level | Mortality Risk | Key Protection |
|---|---|---|
| 30+ grams | 16-23% lower | Cholesterol & blood pressure control |
| Under 15 grams | Baseline risk | Increased health concerns |
Regular consumption improves blood vessel flexibility through nitric oxide production. This helps maintain healthy circulation while reducing strain on the heart. The anti-inflammatory effects are equally impressive – regular consumers show 18% lower C-reactive protein levels.
Maintaining a healthy weight becomes easier with these nutrients. They create lasting fullness, reducing overeating risks. For those recognizing signs of insufficient intake, simple swaps like choosing brown rice over white make significant differences.
Malaysian favorites like oats, lentils, and leafy greens offer delicious ways to boost daily amounts. Combined with professional guidance, these dietary adjustments form a powerful shield against modern health challenges.
Scientific Evidence from Meta-Analyses on Dietary Fiber
Modern nutrition science reaches its strongest conclusions when multiple studies agree. A landmark analysis combined data from 31 separate reviews spanning nearly four decades of research. This approach offers clearer answers than single experiments ever could.
How Researchers Compiled the Data
Scientists used an umbrella review method to analyze existing meta-analyses. They examined papers published between 1980-2017, focusing on English-language publications with strict quality standards. Each included review needed data from at least four randomized trials.
The team evaluated over 71% of these analyses as high-quality. This rigorous process ensured reliable conclusions about plant-based nutrients’ protective effects.
Consistent Protective Patterns Emerge
Every reviewed analysis showed measurable benefits from increased consumption. The most significant impacts appeared in:
| Condition | Risk Reduction | Study Count |
|---|---|---|
| Heart Disease Deaths | 23-33% | 18 reviews |
| New Heart Issues | 9-28% | 22 reviews |
| Stroke Occurrence | 7-17% | 11 reviews |
These patterns held across different populations and study designs. The consistency suggests that boosting daily intake provides reliable protection against circulatory system concerns.

Click to 了解更多
Such robust evidence helps explain why global health organizations prioritize these dietary adjustments. Simple changes in food choices could substantially impact long-term wellness outcomes.
Mechanisms of Dietary Fiber in Lowering Cholesterol
Imagine your body as a complex recycling system where specific nutrients act like specialized cleanup crews. Soluble varieties of plant-based components perform this vital role through biochemical processes that benefit circulation.
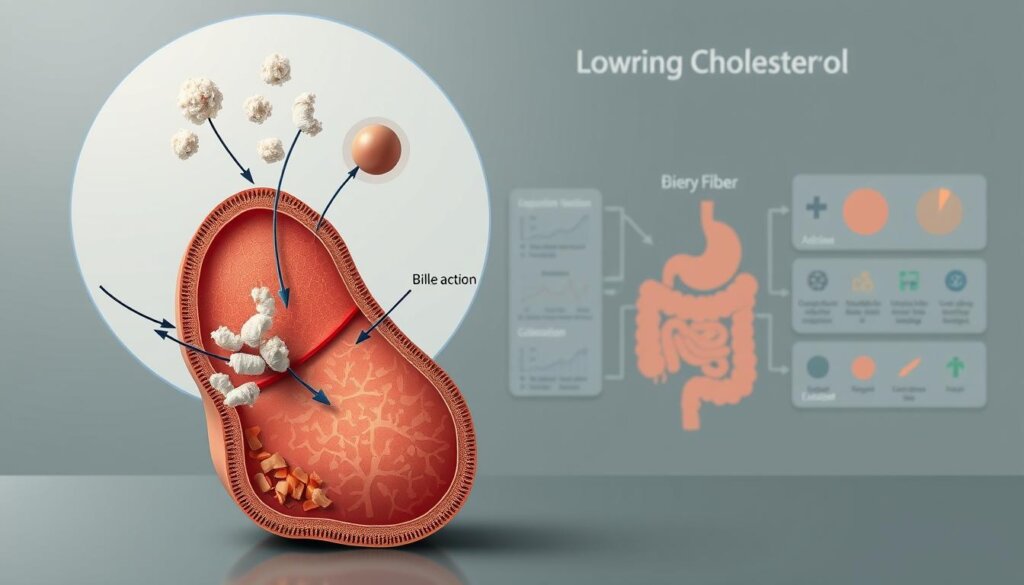
The Bile Acid Connection
These nutrients work like magnets in the digestive tract, binding to bile acids produced from cholesterol. This binding prevents acid reabsorption, forcing the liver to use existing reserves to make new bile. Studies show this process removes 3x more cholesterol than typical elimination methods.
| Supplement Type | Total Cholesterol Reduction | LDL Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| β-Glucan | 12.1 mg/dL | 11.6 mg/dL |
| Psyllium | 13.9 mg/dL | 14.2 mg/dL |
Beyond Basic Elimination
Two additional pathways enhance these effects:
- Modulation of HMG-CoA reductase activity slows new cholesterol production
- Gut bacteria convert these nutrients into fatty acids that regulate lipid metabolism
“Every 10 mg/dL reduction in LDL levels decreases heart event risks by 5-7%.”
The same components improve vessel flexibility through nitric oxide production. This dual action helps maintain healthy blood pressure while addressing cholesterol concerns. Regular consumption creates cumulative benefits that simple medication can’t replicate.
These biological processes explain why global health authorities prioritize dietary adjustments. Small changes in meal choices activate multiple protective mechanisms simultaneously.
Role of β-Glucan and Psyllium in Cardiovascular Health
Could natural compounds hold the key to better cholesterol management? Two plant-based nutrients stand out for their remarkable effects on lipid profiles. β-glucan and psyllium work through unique biological pathways to support circulatory wellness.
Oat-Based Secret Weapon
Found abundantly in oats and mushrooms, β-glucan acts like a cholesterol magnet in the gut. This sticky substance forms thick gels that trap bile acids containing harmful lipids. Research shows daily intake of 4-6 grams delivers impressive results:
| Daily Intake | Total Cholesterol | LDL Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| 4g β-glucan | 5.1-23.2 mg/dL ↓ | 7.3-25.5 mg/dL ↓ |
| 6g β-glucan | 18-23% improvement | 22-25% drop |
“β-glucan’s viscosity directly correlates with cholesterol-lowering capacity – thicker gels remove more lipids.”
Seed-Derived Solution
Psyllium husk from Plantago seeds offers different advantages. Its soluble content creates a gentle sweeping action in digestion. Studies demonstrate 9-10 grams daily helps maintain healthy lipid levels:
| Duration | Total Cholesterol | LDL Change |
|---|---|---|
| 8 weeks | 9.3-14.7 mg/dL ↓ | 10.8-13.5 mg/dL ↓ |
| 6 months | 12-15% reduction | 14-17% drop |
Both nutrients enhance bile acid excretion but work best through different sources. Oatmeal breakfasts provide β-glucan, while psyllium supplements offer concentrated doses. Combining these with whole grains creates powerful dietary synergy for lasting benefits.
Comparing Soluble and Insoluble Fiber Benefits
Not all plant nutrients work the same way in your body—some dissolve, others don’t. Understanding these differences helps create meals that protect your heart while keeping digestion smooth.

Soluble fiber forms a gel when mixed with water. Found in oats, citrus fruits, and beans, this type helps manage cholesterol by trapping bile acids. Popular options like psyllium husk and β-glucan work through this mechanism, as shown in earlier studies.
Insoluble varieties add bulk to meals without dissolving. Whole grains, nuts, and vegetables contain this roughage that speeds food through the digestive system. While it doesn’t directly lower cholesterol, it supports weight control and healthy enzyme production.
| Type | Key Sources | Top Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Soluble | Apples, oats, lentils | Cholesterol reduction Blood sugar balance |
| Insoluble | Brown rice, almonds | Digestive regularity Weight management |
Combining both types delivers the best results. Soluble components tackle cholesterol directly, while insoluble ones improve metabolic health. For example, oatmeal with almond slices provides both varieties in one meal.
Malaysian staples like barley drinks and stir-fried mixed vegetables naturally balance these nutrients. Aim for colorful plates with varied textures to maximize protection against modern health challenges.
Optimal Dietary Fiber Intake Recommendations
How much plant-based nutrition does your daily plate contain? Current guidelines suggest women aim for 25 grams and men 38 grams – yet studies show most people barely reach half these targets. This gap represents a major opportunity for enhancing wellness through simple dietary adjustments.
| Group | Daily Goal | Average Intake |
|---|---|---|
| Women | 25g | 12-15g |
| Men | 38g | 18-20g |
Research confirms maximum protection occurs at 25-35 grams daily for most grown-ups. Older individuals may need slightly less due to metabolic changes, while active persons often require more. Children’s needs grow with age – from 19g at four years to 26g by adolescence.
Three essential tips for success:
- Increase amounts gradually over 2-3 weeks
- Spread consumption across meals
- Pair with adequate hydration
“Sudden spikes in intake can overwhelm digestion – slow adaptation yields better results.”
Custom needs matter. A 70kg office worker needs different amounts than a 90kg athlete. Those managing specific conditions should consult professionals for tailored advice. Timing of consumption also plays a role in maximizing benefits.
Whole foods remain the gold standard – think chickpeas in nasi lemak or oats in bubur. Supplements help bridge gaps but shouldn’t replace nature’s packaging. With smart planning, reaching daily targets becomes both achievable and delicious.
Incorporating High-Fiber Foods into Daily Meals
Transforming daily meals into heart-protective powerhouses begins with smart ingredient swaps. Legumes and whole grains lead the charge, offering concentrated doses of gut-friendly nutrients. A single cup of lentils delivers 15g, while oats provide 4g per serving – perfect for Malaysian breakfast favorites like bubur or roti canai fillings.
Top food sources include chickpeas, barley, and brown rice – staples easily added to nasi lemak or sup tulang. Dark leafy greens like kangkung boost vegetable consumption without sacrificing local flavors. Snack swaps matter too: roasted chickpeas outperform processed crackers in both crunch and nutrition.
Gradual dietary changes prove most sustainable. Start by mixing white and brown rice, then transition fully over weeks. This approach helps digestion adapt while maintaining meal enjoyment. Pairing high-fiber foods with water enhances their benefits, creating lasting fullness between meals.
For time-strapped individuals, pre-cut vegetables and instant oats simplify meal prep. These small shifts align with global nutrition guidelines while honoring Malaysia’s rich food heritage. Consistent consumption builds lasting protection through everyday eating habits.
FAQ
How does dietary fiber connect to heart health?
Eating enough whole grains, fruits, and vegetables supports healthy cholesterol levels and blood pressure. These benefits help reduce strain on arteries, lowering the risk of heart-related issues over time.
What’s the difference between soluble and insoluble types?
Soluble varieties, like oats or beans, dissolve in water to form a gel that traps LDL cholesterol. Insoluble ones, such as wheat bran, add bulk to stool and support digestion without direct heart benefits.
Can psyllium or β-glucan supplements make a difference?
Yes! Psyllium husk binds to bile acids, forcing the liver to use excess cholesterol. β-glucan, found in barley, slows sugar absorption and helps manage lipid profiles. Both are backed by clinical trials for heart support.
How much should someone aim to eat daily?
Adults should target 25–38 grams per day, depending on age and gender. Start slowly to avoid bloating, and prioritize whole foods like lentils, berries, and quinoa over processed options.
Do studies confirm these benefits?
Meta-analyses show a 15–30% lower risk of heart issues with higher intake. Research highlights reduced LDL levels and improved blood vessel function as key factors behind these outcomes.
What meals help boost intake without effort?
Swap white rice for brown, add chia seeds to smoothies, or snack on almonds. Even small changes, like choosing whole-grain bread, add up over weeks to meet daily goals.
Does this nutrient affect blood pressure?
Indirectly, yes. Diets rich in legumes and leafy greens often replace high-sodium processed foods. This shift, paired with better gut health from fiber, supports healthier blood pressure readings.

Khloe Tan
Khloe Tan is a Certified Nutritionist, Corporate Wellness Trainer, and Holistic Health Specialist with over 15 years of experience in the health and wellness industry. She has delivered more than 100 talks nationwide, inspiring and educating diverse audiences on nutrition, lifestyle, and sustainable wellness. Her work has positively impacted over 3,000 lives, and she continues to champion holistic approaches to well-being in both corporate and personal settings.





